Adding modules
On this page, you will learn:
-
How to add a standard and custom module to an application.
-
How to add a module to the local maven repository.
-
How to define when a module should be bootstrapped into the application.
Thus far, we’ve learned about our application descriptor, project structure and application configuration. In the following sections we’ll start adding additional modules in various use cases.
Adding a module
Earlier, you’ve learned that modules are bootstrapped into our application when it starts up.
In this section, a module will be added to the application, by specifying it in the modules parameter of the @AcrossApplication annotation in the application descriptor.
In this example, DebugWebModule will be added to the application.
DebugWebModule enables the user/developer to check various application settings.
See the reference documentation for more information.
Before the module can be added to the application, the jar library needs to be present in the project.
To do so, we’ll specify the dependency in the pom.xml.
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.foreach.across.modules</groupId> (1)
<artifactId>debug-web-module</artifactId> (2)
</dependency>
...
</dependencies>| 1 | The group id of the maven dependency.
The group id specifies the base package prefix, which means that all classes are in a subpackage of com.foreach.across.modules.
All standard modules have com.foreach.across.modules as their group id. |
| 2 | The identifier of the module. |
Versions do not have to be specified explicitly for any of the standard modules if you generate your project through the Across Initializr.
When you’ve downloaded the application from Across Initializr, the latest release version was specified by default.
If you take a look at the dependencyManagement section of the application’s pom file, you’ll notice that there is a dependency on the platform-bom.
The platform-bom is a Bill of Material pom that specifies the module versions of the standard modules, to ensure that those specific versions are compatible.
|
The next step is specifying the module in the application descriptor.
@AcrossApplication( modules = { DebugWebModule.NAME } ) (1)
public class DemoApplication
{
...
}| 1 | Add DebugWebModule to the application. |
Once you’ve restarted the application, you’ll notice that an additional module has been bootstrapped.
... INFO --- [ost-startStop-1] c.f.a.c.AcrossDynamicModulesConfigurer : Adding package based APPLICATION module DemoApplicationModule, resources: demo, base package: com.example.demo.application INFO --- [ost-startStop-1] c.f.a.c.c.bootstrap.AcrossBootstrapper : --- INFO --- [ost-startStop-1] c.f.a.c.c.bootstrap.AcrossBootstrapper : AcrossContext: DemoApplication (AcrossContext-1) INFO --- [ost-startStop-1] c.f.a.c.c.bootstrap.AcrossBootstrapper : Bootstrapping 4 modules in the following order: INFO --- [ost-startStop-1] c.f.a.c.c.bootstrap.AcrossBootstrapper : 1 - AcrossWebModule [resources: ]: class com.foreach.across.modules.web.AcrossWebModule (1) INFO --- [ost-startStop-1] c.f.a.c.c.bootstrap.AcrossBootstrapper : 2 - DebugWebModule [resources: debugweb]: class com.foreach.across.modules.debugweb.DebugWebModule (2) INFO --- [ost-startStop-1] c.f.a.c.c.bootstrap.AcrossBootstrapper : 3 - DemoApplicationModule [resources: demo]: class com.foreach.across.core.DynamicAcrossModule$DynamicApplicationModule INFO --- [ost-startStop-1] c.f.a.c.c.bootstrap.AcrossBootstrapper : 4 - AcrossContextPostProcessorModule [resources: AcrossContextPostProcessorModule]: class com.foreach.across.core.AcrossContextConfigurationModule INFO --- [ost-startStop-1] c.f.a.c.c.bootstrap.AcrossBootstrapper : --- ...
| 1 | AcrossWebModule was added, which provides basic web support for our application.
See Across Web Support for more information. |
| 2 | DebugWebModule was bootstrapped in the application. |
Modules themselves can depend on other modules.
Hence, when DebugWebModule was bootstrapped, AcrossWebModule was bootstrapped as well, because DebugWebModule specifies a required dependency on AcrossWebModule.
Since AcrossWebModule is specified as a dependency in the pom.xml, and is specified as a required dependency, it will be transitively pulled in and bootstrapped as well.
|
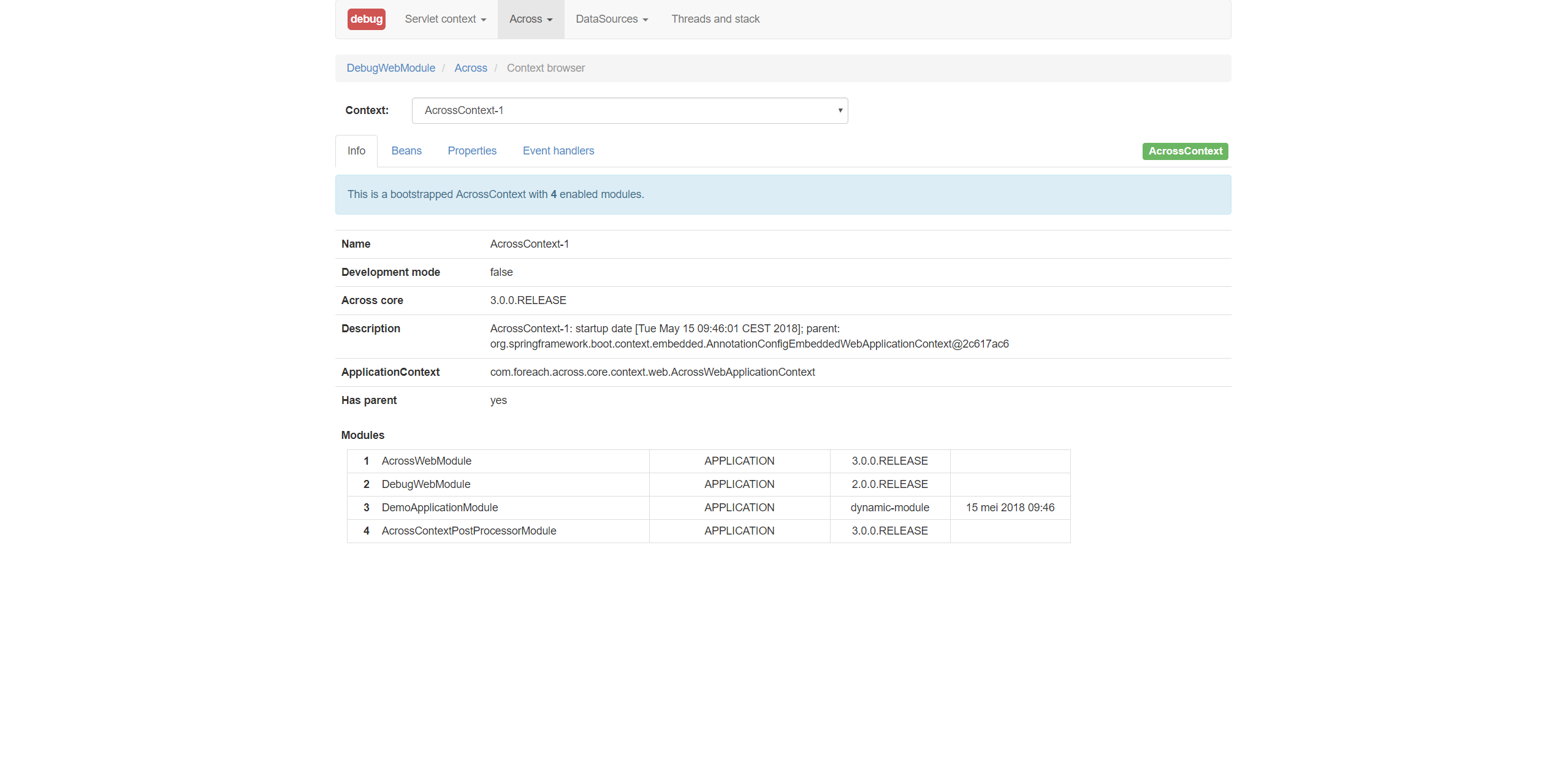
DebugWebModule provides the /debug path, which is a user interface to inspect the application settings.
Amongst these settings, there is a context browser which discloses information about the various Web Contexts that are present in our application, which modules are bootstrapped, which beans are present (in which modules), and more.
We can navigate to the context browser through the Context browser menu item under the Across menu item.
Adding a custom module
You’ve just learned how to add a standard module to your application. Standard modules are supported by the developers of the Across Framework. Across, however, is a framework that enables modular development and encourages a modular approach. As such, other developers are able to create (and contribute!) their own modules, which are the custom modules.
In this section, a custom module will be added to the application. To continue, you’ll first need to clone the module’s project. Before the module is added to the application, we’ll add it to the local maven repository, which is done by executing the following command in the root of the project.
$ mvn clean install
The module can now be added to the application. First the dependency needs to be specified and then we can add it to the application descriptor.
<dependencyManagement> (1)
<dependencies>
...
<dependency>
<groupId>com.foreach.across.samples.modules</groupId>
<artifactId>dummy-module</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
...
<dependency> (2)
<groupId>com.foreach.across.samples.modules</groupId>
<artifactId>dummy-module</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>| 1 | In the dependencyManagement section we define the versions of our application’s dependencies. |
| 2 | The module being added is a custom module, so the group and artifact id are defined by it’s developer.
These are defined in the pom.xml of the module project. |
The module can now be added to the application through the application descriptor. For a module to be bootstrapped in the application, it needs to be found by the Across framework. Across scans for modules based on package names, which by default are the following:
-
com.foreach.across.modules: Across looks for all standard modules that are present. -
modules: Any module specified in themodulepackage on the same level as theapplicationpackage will be found as well.
This means that a custom module is not picked up by Across by default.
To ensure that custom modules are found, scanning for modules can be extended by specifying modulePackages on @AcrossApplication.
@AcrossApplication( modules = { DebugWebModule.NAME, DummyModule.NAME }, modulePackages = { "com.foreach.across.samples.modules" } ) (1)
public class DemoApplication
{
...
}| 1 | Add the group id of dummy module to modulePackages, as well as specifying the module to be imported. |
Once the application is started, the custom module is bootstrapped. The DummyModule serves no purpose and simply creates an additional bean which prints a logging message.
... INFO --- [ost-startStop-1] c.f.a.c.AcrossDynamicModulesConfigurer : Adding package based APPLICATION module DemoApplicationModule, resources: demo, base package: com.example.demo.application INFO --- [ost-startStop-1] c.f.a.c.c.bootstrap.AcrossBootstrapper : --- INFO --- [ost-startStop-1] c.f.a.c.c.bootstrap.AcrossBootstrapper : AcrossContext: DemoApplication (AcrossContext-1) INFO --- [ost-startStop-1] c.f.a.c.c.bootstrap.AcrossBootstrapper : Bootstrapping 5 modules in the following order: INFO --- [ost-startStop-1] c.f.a.c.c.bootstrap.AcrossBootstrapper : 1 - DummyModule [resources: DummyModule]: class com.foreach.across.samples.modules.dummy.DummyModule (1) INFO --- [ost-startStop-1] c.f.a.c.c.bootstrap.AcrossBootstrapper : 2 - AcrossWebModule [resources: ]: class com.foreach.across.modules.web.AcrossWebModule INFO --- [ost-startStop-1] c.f.a.c.c.bootstrap.AcrossBootstrapper : 3 - DebugWebModule [resources: debugweb]: class com.foreach.across.modules.debugweb.DebugWebModule INFO --- [ost-startStop-1] c.f.a.c.c.bootstrap.AcrossBootstrapper : 4 - DemoApplicationModule [resources: demo]: class com.foreach.across.core.DynamicAcrossModule$DynamicApplicationModule INFO --- [ost-startStop-1] c.f.a.c.c.bootstrap.AcrossBootstrapper : 5 - AcrossContextPostProcessorModule [resources: AcrossContextPostProcessorModule]: class com.foreach.across.core.AcrossContextConfigurationModule INFO --- [ost-startStop-1] c.f.a.c.c.bootstrap.AcrossBootstrapper : --- ... INFO --- [ost-startStop-1] c.f.a.c.c.bootstrap.AcrossBootstrapper : --- Starting module bootstrap INFO --- [ost-startStop-1] c.f.a.c.c.bootstrap.AcrossBootstrapper : INFO --- [ost-startStop-1] c.f.a.c.c.bootstrap.AcrossBootstrapper : 1 - DummyModule [resources: DummyModule]: class com.foreach.across.samples.modules.dummy.DummyModule INFO --- [ost-startStop-1] c.f.a.c.c.w.AcrossWebApplicationContext : Refreshing DummyModule: startup date [Tue May 22 09:38:38 CEST 2018]; parent: AcrossContext-1 INFO --- [ost-startStop-1] c.f.a.c.c.w.AcrossWebApplicationContext : Registering annotated classes: [class com.foreach.across.core.config.CommonModuleConfiguration,class com.foreach.across.core.config.ModuleConfigurationImportSelector,class com.foreach.across.config.IllegalConfigurationValidator$IllegalConfigurationDetector] INFO --- [ost-startStop-1] f.a.AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor : JSR-330 'javax.inject.Inject' annotation found and supported for autowiring INFO --- [ost-startStop-1] c.f.a.c.d.AcrossDevelopmentMode : Across development mode active: true INFO --- [ost-startStop-1] c.f.a.c.d.AcrossDevelopmentMode : Loading development properties from URL [file:C:/Users/steven/dev-configs/across-devel.properties] INFO --- [ost-startStop-1] c.f.a.s.m.d.c.DummyModuleConfiguration : DummyModule has been added to the application. (2) ...
| 1 | The custom module has been bootstrapped into the application. |
| 2 | The DummyModule simply prints an additional log message during startup. |
Conditional modules
In the previous sections, you’ve learned how to add modules by using the @AcrossApplication annotation.
It is also possible to specify a module by defining it as a bean.
When a module is defined as a bean, it will be added to the ApplicationContext, but since a module always implements the AcrossModule interface, it will also be picked up by the AcrossContext.
By using this approach, Spring annotations can be used to define when exactly the module should be created.
In the following examples, you’ll add DebugWebModule to the application once again, but instead of specifying the module by name, you’ll add it as a bean.
First off, you’ll add the module when starting the application with the dev profile.
If you haven’t read about application profiles yet, take a look at Application profiles.
@AcrossApplication( modules = { } )
public class DemoApplication
{
...
@Bean (1)
@Profile("dev") (2)
public DebugWebModule debugWebModule(){
return new DebugWebModule(); (3)
}
}| 1 | We specify the module as a bean so that it can be picked up by the AcrossContext. |
| 2 | We specify the @Profile annotation so that it is only added when the dev profile is active. |
| 3 | We return an instance that will be bootstrapped as a module. |
If we would now simply start up the application again, we would notice that neither DebugWebModule nor AcrossWebModule are bootstrapped into the application.
... INFO --- [ restartedMain] com.example.demo.DemoApplication : No active profile set, falling back to default profiles: default (1) ... INFO --- [ost-startStop-1] c.f.a.c.AcrossDynamicModulesConfigurer : Adding package based APPLICATION module DemoApplicationModule, resources: demo, base package: com.example.demo.application INFO --- [ost-startStop-1] c.f.a.c.c.bootstrap.AcrossBootstrapper : --- INFO --- [ost-startStop-1] c.f.a.c.c.bootstrap.AcrossBootstrapper : AcrossContext: DemoApplication (AcrossContext-1) INFO --- [ost-startStop-1] c.f.a.c.c.bootstrap.AcrossBootstrapper : Bootstrapping 2 modules in the following order: (2) INFO --- [ost-startStop-1] c.f.a.c.c.bootstrap.AcrossBootstrapper : 1 - DemoApplicationModule [resources: demo]: class com.foreach.across.core.DynamicAcrossModule$DynamicApplicationModule INFO --- [ost-startStop-1] c.f.a.c.c.bootstrap.AcrossBootstrapper : 2 - AcrossContextPostProcessorModule [resources: AcrossContextPostProcessorModule]: class com.foreach.across.core.AcrossContextConfigurationModule INFO --- [ost-startStop-1] c.f.a.c.c.bootstrap.AcrossBootstrapper : --- ...
| 1 | We started the application without any profile, so only the 'default' profile is present. |
| 2 | Neither DebugWebModule nor AcrossWebModule have been bootstrapped. |
If we would then start up the application with the dev profile, these modules will be bootstrapped once again.
$ mvn spring-boot:run -Dspring-boot.run.profiles=dev
... INFO --- [ restartedMain] com.example.demo.DemoApplication : The following profiles are active: dev (1) ... INFO --- [ost-startStop-1] c.f.a.c.AcrossDynamicModulesConfigurer : Adding package based APPLICATION module DemoApplicationModule, resources: demo, base package: com.example.demo.application INFO --- [ost-startStop-1] c.f.a.c.c.bootstrap.AcrossBootstrapper : --- INFO --- [ost-startStop-1] c.f.a.c.c.bootstrap.AcrossBootstrapper : AcrossContext: DemoApplication (AcrossContext-1) INFO --- [ost-startStop-1] c.f.a.c.c.bootstrap.AcrossBootstrapper : Bootstrapping 4 modules in the following order: (2) INFO --- [ost-startStop-1] c.f.a.c.c.bootstrap.AcrossBootstrapper : 1 - AcrossWebModule [resources: ]: class com.foreach.across.modules.web.AcrossWebModule INFO --- [ost-startStop-1] c.f.a.c.c.bootstrap.AcrossBootstrapper : 2 - DebugWebModule [resources: debugweb]: class com.foreach.across.modules.debugweb.DebugWebModule INFO --- [ost-startStop-1] c.f.a.c.c.bootstrap.AcrossBootstrapper : 3 - DemoApplicationModule [resources: demo]: class com.foreach.across.core.DynamicAcrossModule$DynamicApplicationModule INFO --- [ost-startStop-1] c.f.a.c.c.bootstrap.AcrossBootstrapper : 4 - AcrossContextPostProcessorModule [resources: AcrossContextPostProcessorModule]: class com.foreach.across.core.AcrossContextConfigurationModule INFO --- [ost-startStop-1] c.f.a.c.c.bootstrap.AcrossBootstrapper : --- ...
| 1 | We have started the application with the dev profile. |
| 2 | DebugWebModule and AcrossWebModule are bootstrapped as well. |
@AcrossApplication( modules = { } )
public class DemoApplication
{
...
@Bean (1)
@ConditionalOnProperty("dev") (2)
public DebugWebModule debugWebModule(){
return new DebugWebModule(); (3)
}
}